
It will take more than a long-term target for 2050 to achieve climate neutrality, says Reto Knutti. Policymakers must take a consistent approach towards net zero, and define a reduction path with specific measures and interim targets.
>Read the article in English (ethz.ch), By Prof. Reto Knutti, ETHZ
>and in German
We're on track to true climate catastrophe's. This is what we are facing!
What is the problem?
Global mean surface temperatures reached 1.2°C above the pre-industrial average in 2020, and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change warned in its recent report that Earth could hit 1.5°C in as little as a decade. The 0.3°C separating these two temperatures make a world of difference. Scientists believe that stabilising our warming world’s temperature at 1.5°C could help avoid the most serious effects of climate change.
What do we have to do?
Fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas are the source of just over 80% of the world’s energy. Burning them accounts for 89% of human-derived CO₂ emissions. To avert catastrophic warming, the global community must rapidly reduce how much of these fuels it extracts and burns. Our new paper, published in Nature, revealed just how tight the world’s remaining carbon budget is likely to be.
In order to hold global warming at 1.5°C, we found that nearly 60% of global oil and fossil gas reserves will need to remain in the ground in 2050. Almost all of the world’s coal – 90% – will need to be spared from factory and power plant furnaces. Our analysis also showed that global oil and gas production must peak immediately and fall by 3% each year until mid-century. More...
Anabel and I found an amazing article on global warming. Since it is a very long article, we decided to split the work between the two of us. I am going to talk about communication of facts and causes. Anabel will write about the effects and measures.
Global warming
Global warming is the phenomenon of increasing average air temperatures of the earth. Since the middle of the 20th century, climate scientists have gathered (zusammentragen, sammeln) detailed observations of various weather phenomena and of related influences on climate.
Facts
The global warming: Increase in the global average surface temperature resulting from enhancement of the greenhouse effect, primarily by air pollution.
Many scientists predict that such an increase of the temperature would cause polar ice caps (Eisschicht) and mountain glaciers to melt rapidly significantly raising the levels of coastal waters (Küstengewässer) and would produce extremes of drought (Dürre) and rainfall, seriously disrupting (beeinträchtigen) food production in certain regions.
Causes
A special report noting that human beings and human activities have been responsible for a worldwide average temperature increase of between 0.8 and 1.2 °C of global warming since preindustrial times, and most of the warming observed over the second half of the 20th century could be attributed to human activities.
The predicted rise in temperature was based on a range of possible scenarios that accounted for future greenhouse gas emissions and mitigation (Eindämmung, Minderung) (severty reduction) (Armutsreduzierung) measures and on uncertainties.
Effects
- Significant societal, economic and ecological damage.
- Should carbon emissions continue at their present rate, the increase in average near-surface air temperatures would reach 1.5 °C sometime between 2030 and 2052.
Measures
- By 2015 all but a few national governments had begun the process of instituting carbon reduction plans as a part of the Paris Agreement.
- A rapid transition away from fossil fuel energy.

If you are interested in reading the whole article, here goes to the Article (britannica.com).
Climate researcher Sonia Seneviratne contributed to the latest assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). As she highlights here, the new report clearly demonstrates that we can’t afford to lose any more time when it comes to climate change.
>To the full article in English and German (futureblog of ethz.ch)
What is the state of the art regarding climate change?
You check it out here (watson.ch, in German)
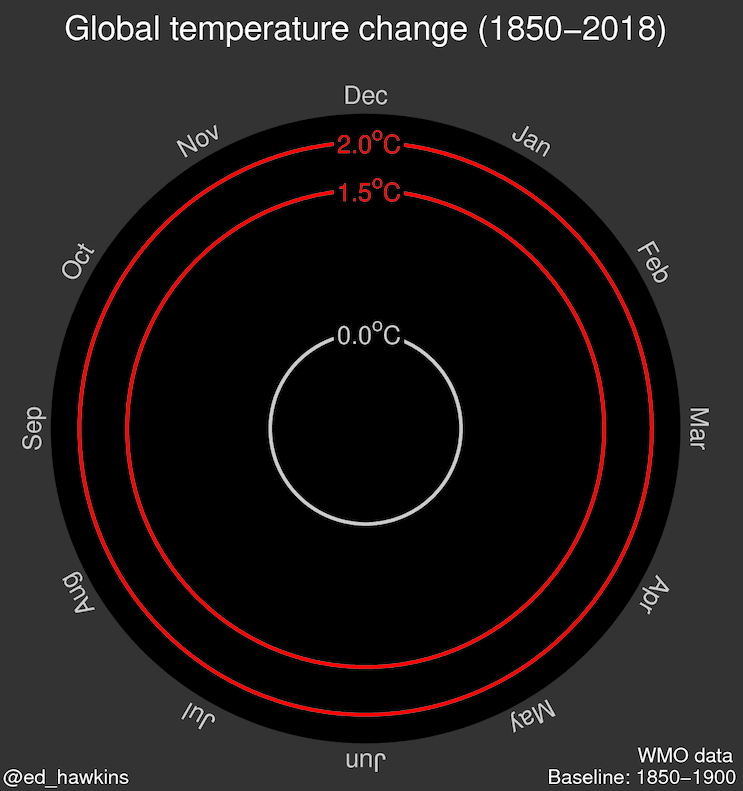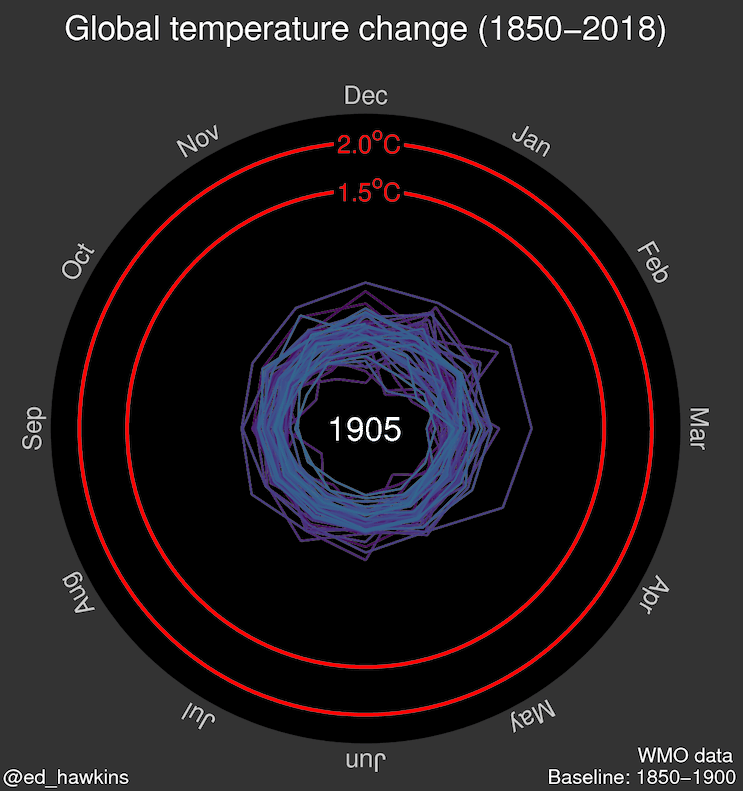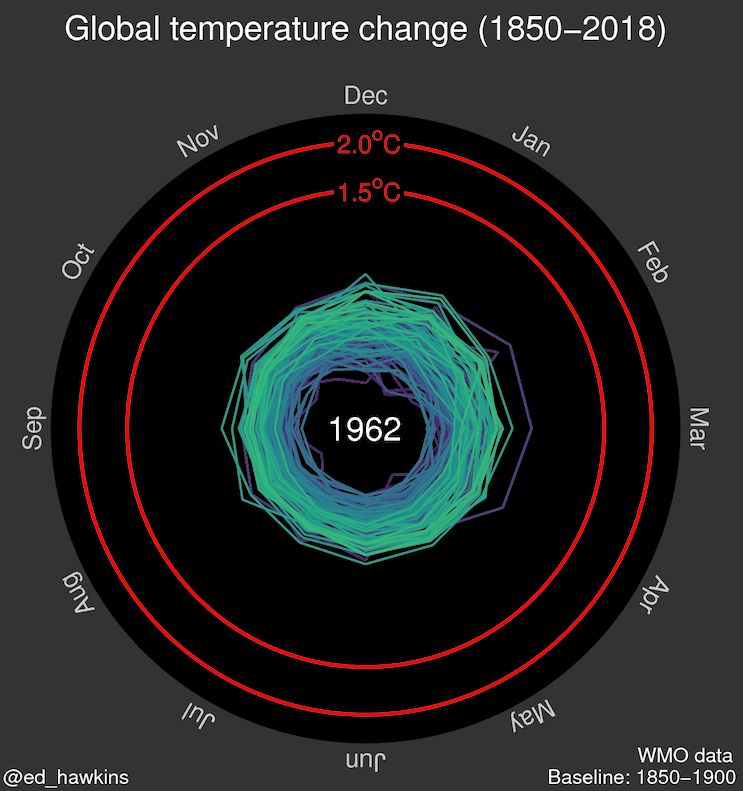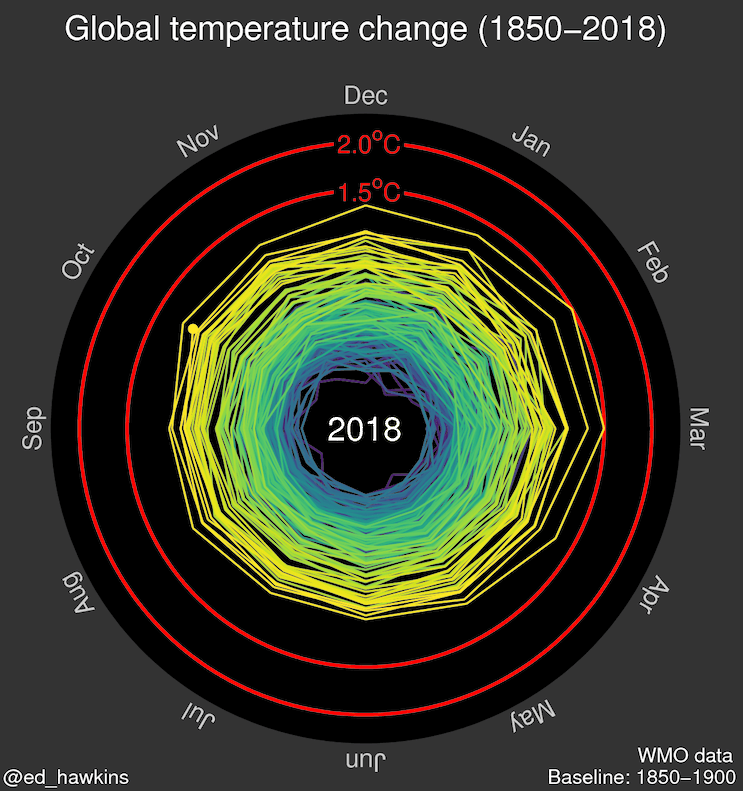
Source: Climate spiral (wikipedia.org)
Hey everyone !!
A survey on floods in Kerala was conducted on 11th May 2021 and click here to view the detailed results.
.png)
.png)
Hope you found our work interesting !! Looking forward to your comments.
Thank you !!
Team - Maya ma'am, Devanarayan, Vamika Giridhar, Johanna Christy, Ananya Reji
Source: MCC (mcc-berlin.net)
Timelines by Fabian Oefner
more videos accessible.
About Fabian Oefner and the making of:
Screenshot from the video below:

Legacy of an Arctic pioneer (Vermächtnis eines Arktis-Pioniers) More...